A good credit score is crucial for securing loans, credit cards, and favourable interest rates. It reflects your creditworthiness and financial responsibility, influencing lenders’ decisions and even impacting employment opportunities in some cases. Whether you’re looking to rebuild your credit or improve an already decent score, this comprehensive guide will provide you with actionable steps to enhance your credit score effectively.
Understanding Credit Scores
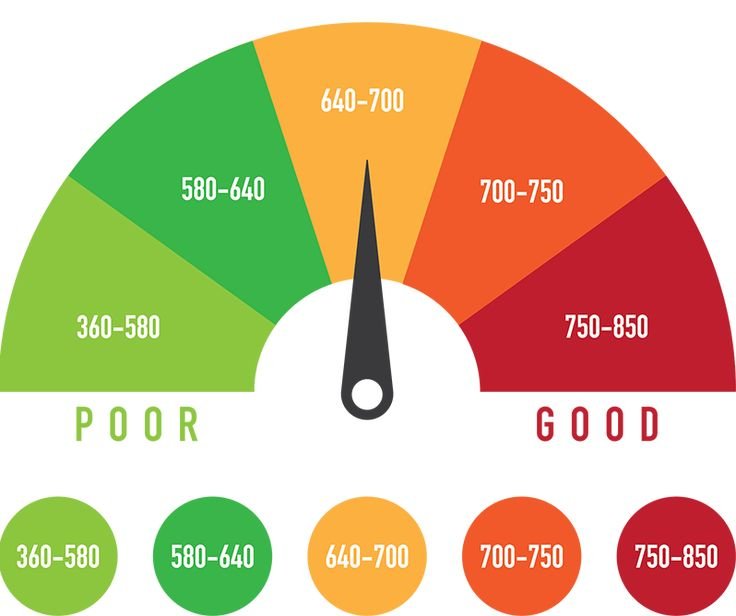
Credit scores are numerical representations of your creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850. They are calculated based on several factors, including your payment history, credit utilisation, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and recent credit inquiries. The most commonly used credit scoring models are FICO and VantageScore.
Credit Score Ranges:
– Excellent: 750 – 850
– Good: 700 – 749
– Fair: 650 – 699
– Poor: 600 – 649
– Very Poor: 300 – 599
Steps to Improve Your Credit Score
- Check Your Credit Report
Start by obtaining your credit reports from the three major credit bureaus—Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. You can get a free report from each bureau annually at AnnualCreditReport.com. Review your reports for any errors or discrepancies that could be negatively affecting your score.
Key Actions:
– Dispute inaccuracies with the credit bureau.
– Ensure all personal information is correct.
– Look for signs of identity theft or fraudulent accounts.
- Pay Your Bills on Time
Payment history is the most significant factor in your credit score, accounting for 35% of your FICO score. Consistently paying your bills on time demonstrates financial responsibility and positively impacts your credit score.
Key Actions:
– Set up automatic payments for recurring bills.
– Use reminders or calendar alerts for payment due dates.
– Catch up on any past-due accounts as soon as possible.
- Reduce Your Credit Utilisation Ratio
Your credit utilisation ratio is the amount of credit you’re using compared to your credit limits. Aim to keep your credit utilisation below 30% to maintain a good credit score.
Key Actions:
– Pay down high balances on credit cards.
– Request a credit limit increase to improve your utilisation ratio.
– Avoid closing credit card accounts, as this can decrease your available credit.
- Avoid Opening Too Many New Accounts at Once
Each time you apply for new credit, a hard inquiry is made on your credit report, which can temporarily lower your score. Multiple inquiries in a short period can have a more significant impact.
Key Actions:
– Limit new credit applications.
– Research and apply for credit only when necessary.
– Consider pre-qualification offers that don’t impact your credit score.
- Maintain a Mix of Credit Accounts
Having a variety of credit types, such as credit cards, auto loans, and mortgages, can positively affect your credit score. It shows lenders you can manage different types of credit responsibly.
Key Actions:
– Don’t shy away from instalment loans if you need them.
– Keep older accounts open to maintain a longer credit history.
– Avoid taking on too much debt just to diversify your credit mix.
- Monitor Your Credit Regularly
Regular monitoring of your credit can help you stay on top of changes and quickly address any issues that arise. Many services offer free credit monitoring and alerts.
Key Actions:
– Sign up for credit monitoring services.
– Check your credit score monthly through free platforms.
– Immediately investigate any unexpected changes to your score.
- Become an Authorised User
Being added as an authorised user on someone else’s credit card account can help boost your credit score, provided the primary user has good credit habits.
Key Actions:
– Choose someone with a good credit history.
– Ensure the account has a low balance and positive payment history.
– Verify that the credit card issuer reports authorised user activity to the credit bureaus.
- Pay Off Debt Strategically
Focus on paying off debt to reduce your overall debt burden and improve your credit score. Prioritise high-interest debt first, but also consider the impact on your credit utilisation ratio.
Key Actions:
– Use the avalanche method (paying off high-interest debt first) or the snowball method (paying off small balances first).
– Consolidate debt with a lower interest loan if feasible.
– Avoid accumulating new debt while paying off existing balances.
Conclusion
Improving your credit score is a process that requires diligence, patience, and strategic financial management. By understanding the factors that influence your credit score and taking proactive steps to address them, you can enhance your creditworthiness and open up better financial opportunities. Regularly monitor your credit, make timely payments, manage your debt responsibly, and avoid common pitfalls to achieve and maintain a good credit score.
A strong credit score not only facilitates access to credit at favourable terms but also reflects positively on your overall financial health. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can build a solid credit foundation and enjoy the benefits of improved creditworthiness.






